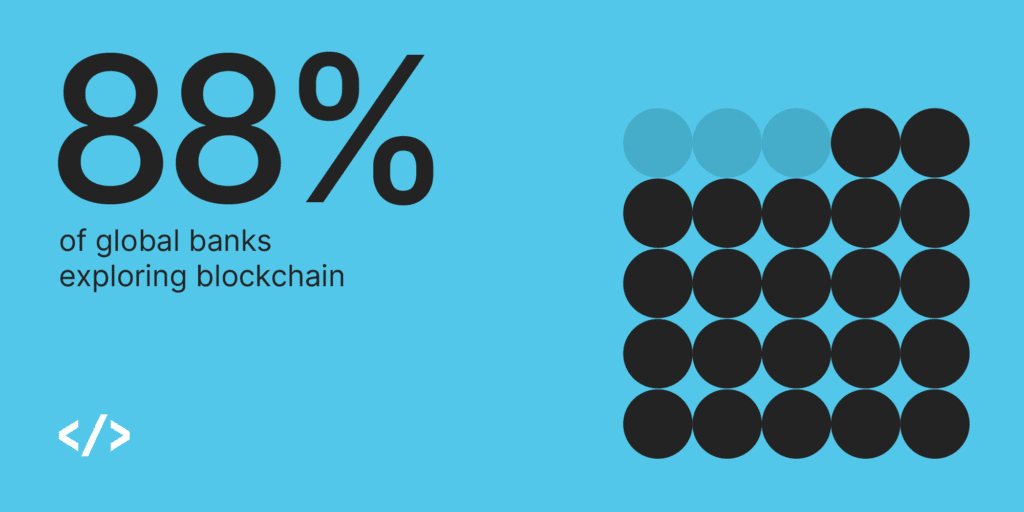
The maturation of blockchain technology, combined with increasing regulatory clarity, has accelerated its adoption by large financial institutions. With 88% of global banks announcing or exploring blockchain-based services, the shift toward modernizing financial infrastructure is clear.
But what does crypto institutionalization actually look like today? Why are traditional and decentralized financial infrastructures (DeFi) beginning to overlap, and what should leaders focus on as crypto enters its regulated institutional phase?

What Crypto Institutionalization Really Means
There is a new era of liquidity, regulation and technological maturity that blurs the lines between TradFi and decentralized finance.
Institutional adoption of crypto goes well beyond hedge funds buying Bitcoin. It now includes licensed custody and trading platforms, AML/KYC compliant DeFi protocols, and tokenized real-world assets (RWA). Large banks are also entering the market and experimenting with stablecoin and blockchain-based settlement systems that offer speed, transparency and cost-effectiveness.
Recent endorsements from financial giants such as BlackRock, Fidelity and JPMorgan through Bitcoin and Ethereum spot ETFs have propelled digital assets into the mainstream. Custodians like BNY Mellon are expanding regulated custody of cryptocurrencies, while projects like JPMorgan’s Onyx and Société Générale’s EURCV stablecoin demonstrate how blockchain infrastructure is integrated into global banking operations.
This institutionalization of digital assets represents a systemic integration of blockchain into the regulated financial ecosystem. Crypto is evolving from an asset class to the infrastructure layer upon which modern finance relies. For example, Stablecoins could represent up to 10% of the global money supply by 2034, serving as a bridge between TradFi efficiency and DeFi innovation.
Institutionalization is a mutual transformation as crypto adapts to regulatory and operational frameworks, TradFi evolves to exploit the technological advantages of blockchain. The result is not convergence per se, but the creation of a hybrid financial infrastructure designed for scale, security and innovation.
Why TradFi is adopting crypto
The past few years have been transformative for institutional engagement with digital assets. The SEC’s approval of 10 spot Bitcoin ETFs in early 2024 marked a defining moment. In just a few months, Bitcoin ETFs have accumulated over $100 billion in assets under management, solidifying the institutional adoption of crypto as a key driver of market liquidity.
Ethereum ETFs quickly followed, further boosting institutional confidence. Large banks and asset managers like BNY Mellon have begun offering regulated custody of cryptocurrencies, aligning with the new SEC and MiCA frameworks to provide secure access to clients.
TradFi’s adoption of crypto is not driven by speculation but by strategic modernization. Institutions view blockchain as a tool to:
-
Increase operational efficiency with instant settlement and reduced reconciliation costs.
-
Unlock new sources of income through tokenization and digital asset products.
-
Meet customer demand for regulated exposure to crypto markets.
From BlackRock’s tokenized money market fund to Deutsche Bank’s digital custody partnerships, the evidence is clear: digital asset infrastructure is no longer peripheral as it becomes central to institutional strategy.
Regulation: a bridge or a barrier?
Historically, uncertainty surrounding regulation has been one of the biggest barriers to institutional adoption of crypto. Today, it becomes a catalyst for growth.
The introduction of MiCA (Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulatory) in the EU has set a global benchmark, providing legal clarity for service providers and investors. At the same time, the Basel III framework and SEC ETF approvals have brought much-needed standardization and legitimacy to the sector.
These developments have transformed the landscape, reducing volatility and enabling regulated access to digital assets through licensed platforms and compliant custody solutions. Institutions can now engage in digital asset tokenization and trading with confidence, knowing that risk, capital and disclosure requirements are aligned with global standards.
Now, regulation is no longer an obstacle; this is the foundation of trust support institutional participation in the digital economy.
What DeFi learns from TradFi
While TradFi embraces the transparency and automation of blockchain, DeFi borrows from the risk management and compliance disciplines of traditional finance.
Protocols like Aave Arc now offer permissioned liquidity pools with KYC verification, catering specifically to institutional participants. Governance mechanisms, reporting standards and capital adequacy models, long-standing features of TradFi, are increasingly replicated within DeFi ecosystems.
This hybridization produces a new model often referred to as CeDeFi (centralized and decentralized financial systems), where decentralized technologies operate within regulated frameworks. It allows institutions to benefit from the efficiency of DeFi while maintaining security and accountability through regulated crypto custody and audited infrastructure.
Concrete examples reinforce this convergence:
-
JPMorgan’s DeFi-based collateral settlement using tokenized assets.
-
BlackRock’s BUIDL fundwhich is an offering of real-world tokenized assets.
-
Franklin Templeton’s OnChain Mutual Fundconnecting DeFi transparency to traditional surveillance.
DeFi is no longer on the outside looking in; it becomes a critical part of the institutional-grade digital asset infrastructure that powers the next phase of financial innovation.
What comes next?

The convergence of crypto and TradFi is no longer a theoretical exercise; it is a strategic reality that is reshaping the future of finance.
In the near term, the continued expansion of tokenized real-world assets (RWA), stable payment rails, and regulated custody will drive institutional engagement. By 2030, tokenized assets could exceed $10 trillion, unlocking liquidity in previously illiquid markets.
Longer term, the global financial ecosystem will become increasingly hybridized, combining the transparency and programmability of blockchain with the compliance and scale of TradFi. We can expect:
-
Greater integration between banks and DeFi protocols.
-
More liquidity and interoperability between chains between digital asset networks.
-
The rise of programmable finance, where smart contracts automate settlements and reporting.
For institutional leaders, this moment represents a critical moment. Strategic considerations include:
-
In partnership with regulated digital asset infrastructure suppliers.
-
Explore tokenization pilot projects for bonds, funds and alternative assets.
-
Develop internal expertise around compliance, smart contracts and DeFi risk frameworks.
Conclusion
The institutionalization of crypto marks a structural transformation in the functioning of global finance. TradFi and DeFi are no longer opposing forces, but rather complementary layers of a unified financial ecosystem.
For financial institutions, this convergence brings greater efficiency, accessibility and diversification. The opportunity lies in understanding how to manage this transition by combining the credibility of TradFi with the innovation of DeFi to provide secure, scalable and compliant solutions.
As blockchain technology becomes integrated into the very heart of financial markets, the message is clear:
Institutions that adopt regulated digital asset infrastructure today will define the next chapter of global finance.
Learn how Bitpanda Technology Solutions enables financial institutions to participate in the future of regulated digital asset infrastructure.
Contact us today to find out more.
Disclaimer
This article is distributed for informational purposes and should not be construed as an offer or recommendation. It does not constitute and cannot replace investment advice.
Bitpanda makes no representations or warranties as to the accuracy and completeness of the information contained herein.
Investing involves risks. You could lose all the money you invest.