Article Highlight | 31-October-2025
picture:
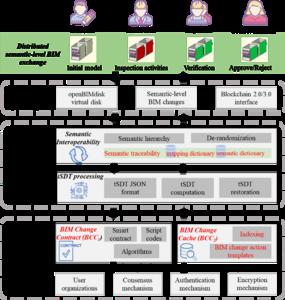
The framework consists of three layers from top to bottom: (1) the application layer, (2) the tSDT approach, and (3) the Blockchain 3.0 framework. The topmost application layer, which hosts a web-based DApp named openBIMdisk, connects to the distributed BIM exchange.
see more
Credits: Lingming KONG 1, Rui ZHAO 1, Chimay J. ANUMBA 2, Weisheng LU 1, Fan XUE 1, †
This study is led by Professor Xue Fan (iLab, Faculty of Architecture, University of Hong Kong). The team proposed a new blockchain-enabled Open BIM data exchange paradigm to facilitate effective collaboration.
The research team found that the traditional file-based Open BIM data exchange approach faces redundancy, traceability, and security challenges. Inspired by the nature of incremental development of BIM and Blockchain technology, capturing incremental changes in BIM as transactions and exchanges occur via a blockchain network may be a solution. First, a new tSDT approach is presented. The tSDT uses a semantic traceability function, which systematizes the modified semantic identifiers to generate two mapping dictionaries, to resolve the dilemma between data redundancy and traceability. Then, the reduced BIM semantic changes are captured via tSDT to be exchanged in a Hyperledger Fabric blockchain network. openBIMdisk, a web application with intuitive user interfaces, implements tSDT and Blockchain.
The proposed tSDT approach and blockchain-based data exchange paradigm were applied to a real integrated modular construction project. Experimental results indicated that tSDT achieved minimal BIM redundancy for storing and restoring all BIM changes, using an average of 0.007% of disk space. openBIMdisk facilitated BIM version management and object-level semantic traceability with a response time of 5.3 ms.
See the article: Open BIM exchange on virtual disk Blockchain 3.0: A traceable semantic differential transactional approach