North Korean hacker group Konni (Opal Sleet, TA406) is using AI-generated PowerShell malware to target developers and engineers in the blockchain industry.
Believed to be associated with the APT37 and Kimsuky clusters, Konni has been active since at least 2014 and has been seen targeting organizations in South Korea, Russia, Ukraine, and various countries in Europe.
Based on samples analyzed by Check Point researchers, the threat actor’s latest campaign focuses on targets in the Asia-Pacific region, with the malware having been submitted from Japan, Australia, and India.

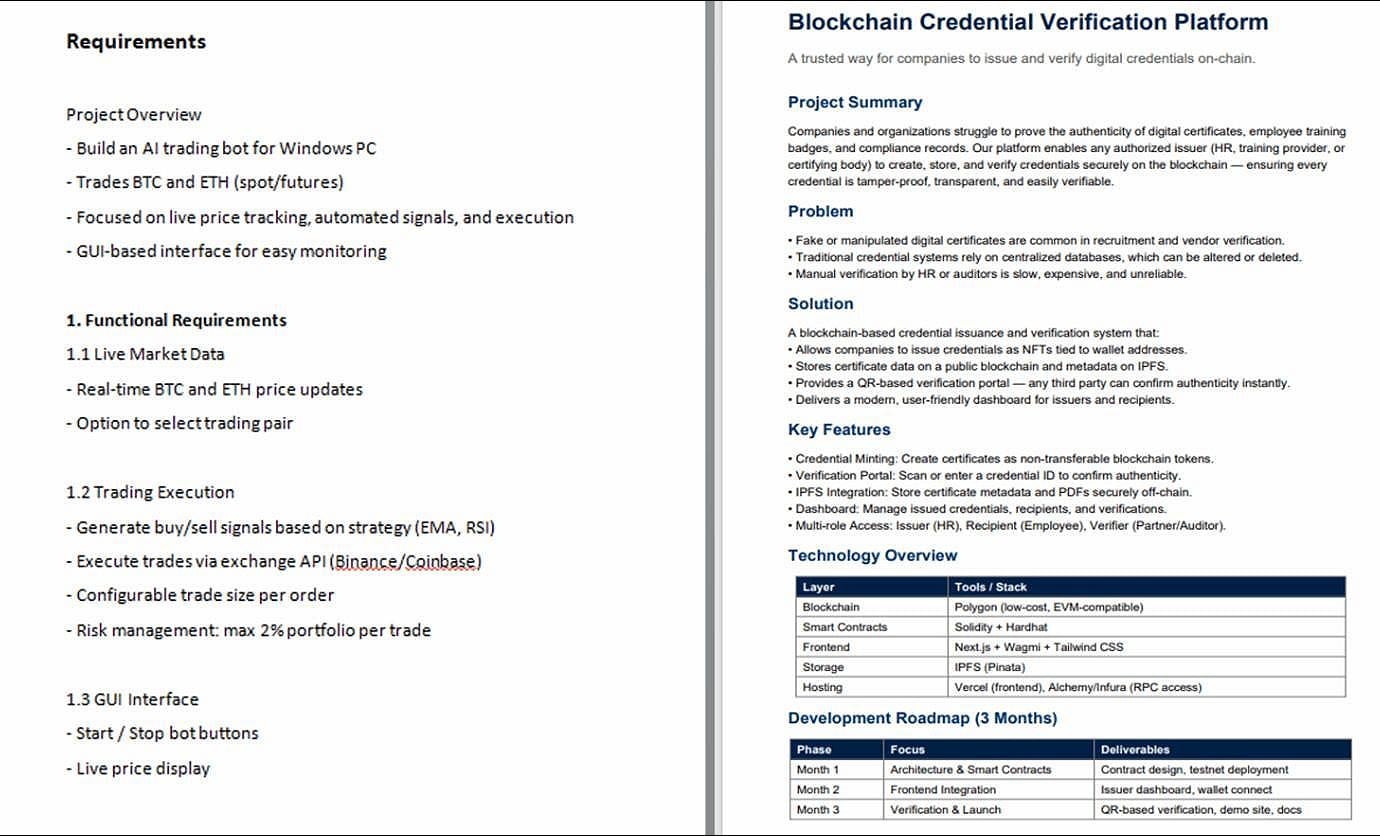
The attack begins when the victim receives a link hosted on Discord that provides a ZIP archive containing a decoy PDF and a malicious LNK shortcut file.
The LNK runs an embedded PowerShell loader that extracts a DOCX document and a CAB archive containing a PowerShell backdoor, two batch files, and a UAC bypass executable.
Launching the shortcut file opens the DOCX and executes a batch file included in the CAB file.
Source: Checkpoint
The DOCX decoy document suggests that hackers want to compromise development environments, which could provide them with “access to sensitive assets, including infrastructure, API credentials, wallet access, and ultimately cryptocurrency holdings.”
The first batch file creates a staging directory for the backdoor and the second batch file, and creates an hourly scheduled task masquerading as a OneDrive startup task.
This task reads an XOR-encrypted PowerShell script from disk and decrypts it for execution in memory. Finally, it removes itself to erase the signs of infection.
Source: Checkpoint
AI-generated backdoor
The PowerShell backdoor itself is heavily obfuscated using arithmetic-based string encoding, execution string reconstruction, and execution of final logic via “Invoke-Expression”.
The researchers say the PowerShell malware “strongly indicates AI-assisted development rather than traditional operator-created malware.”
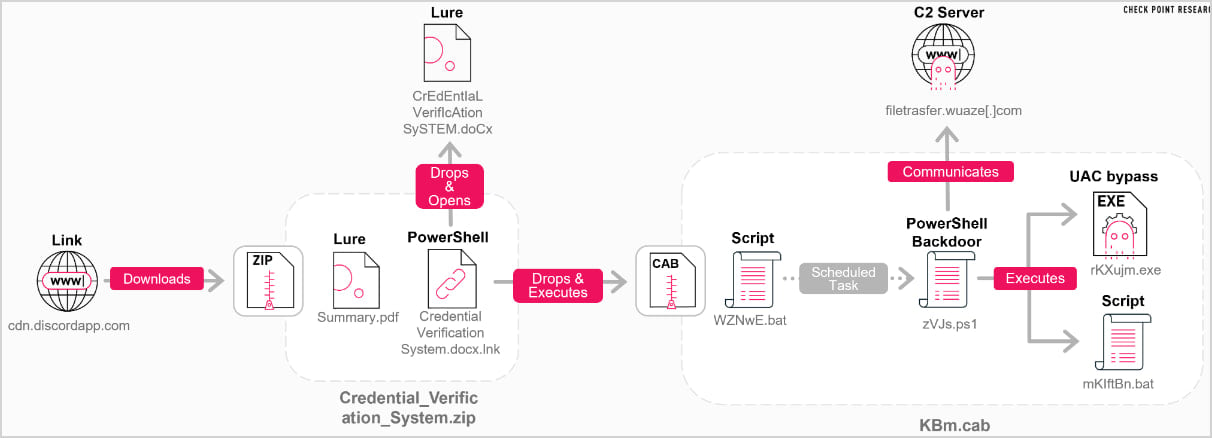
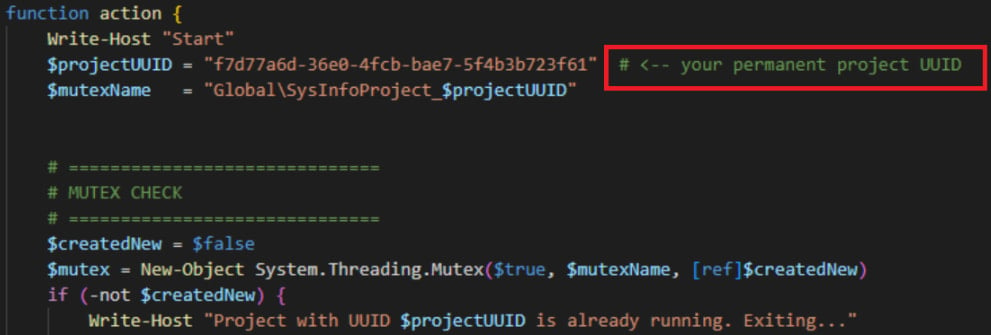
Evidence leading to this conclusion includes the clear, structured documentation at the top of the script, which is unusual for malware development; its modular and refined layout; and the presence of a comment “# <– your permanent project UUID”.
Source: Checkpoint
“This wording is very characteristic of LLM-generated code, where the model explicitly tells a human user how to customize a placeholder value,” Check Point explains.
“Such comments are commonly seen in AI-produced scripts and tutorials.”
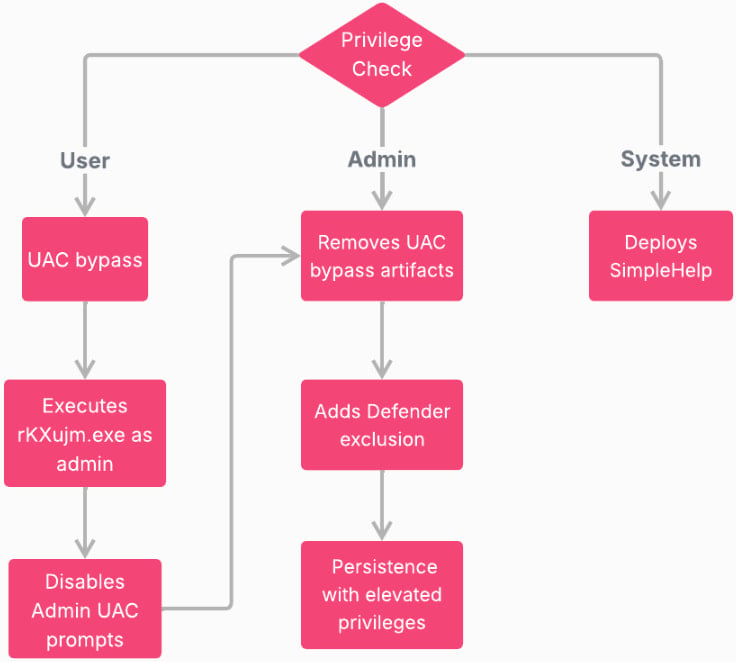
Before execution, the malware performs checks of hardware, software, and user activity to ensure that it is not running in scanning environments, then generates a unique host ID.
Then, based on the execution privileges it has on the compromised host, it follows a separate path of action, as shown in the following diagram.
Source: Checkpoint
Once the backdoor is fully operational on the infected device, it periodically contacts the command and control (C2) server to send basic host metadata and polls the server at random intervals.
If the C2 response contains PowerShell code, it turns it into a script block and executes it asynchronously through background tasks.
Check Point attributes these attacks to threat actor Konni based on previous launcher formats, overlapping file names and script names, and commonalities in execution chain structure with previous attacks.
Researchers have released Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) associated with this recent campaign to help defenders protect their assets.

Whether you want to clean up old keys or set guardrails for AI-generated code, this guide helps your team build securely from the start.
Get the cheat sheet and take the guesswork out of managing secrets.




